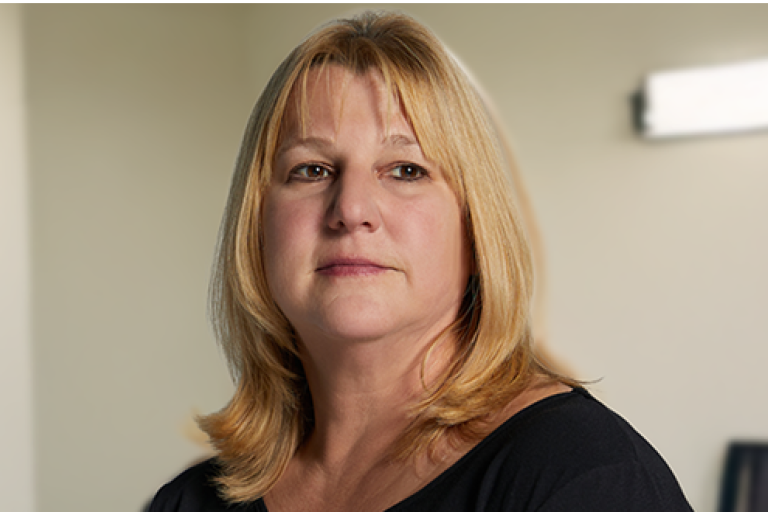

Jill, a high school superintendent living with recurrent pericarditis
Preparing for your visit
Given that recurrent pericarditis is a rare disorder, it’s possible that your doctor may not be familiar with your symptoms and treatment options. That’s why it’s important to plan in advance so you can get the most out of your visit. Even if you’re seeing a specialist, be sure to come prepared so you can ask the right questions to help receive the best possible care.
Starting a conversation with your doctor
Start by telling your doctor if you were previously diagnosed with pericarditis and what type. If you have been diagnosed, your doctor can confirm; if you haven’t, you might ask your doctor to consider the possibility.
If you've had previous flares, be sure to tell your doctor this is not the first time you've experienced these symptoms.
If recurrent pericarditis has caused you anxiety or depression, you are not alone. Individuals with recurrent pericarditis have reported that the condition can affect their emotions and quality of life.
Tell your doctor if you have recently experienced the following symptoms:
- Feeling anxious
- Sleeplessness
- Interruption in your daily routine
- Fear of your next flare
- Missing time at work
- Feeling depressed
Be sure to include how long they have been happening and how many times.
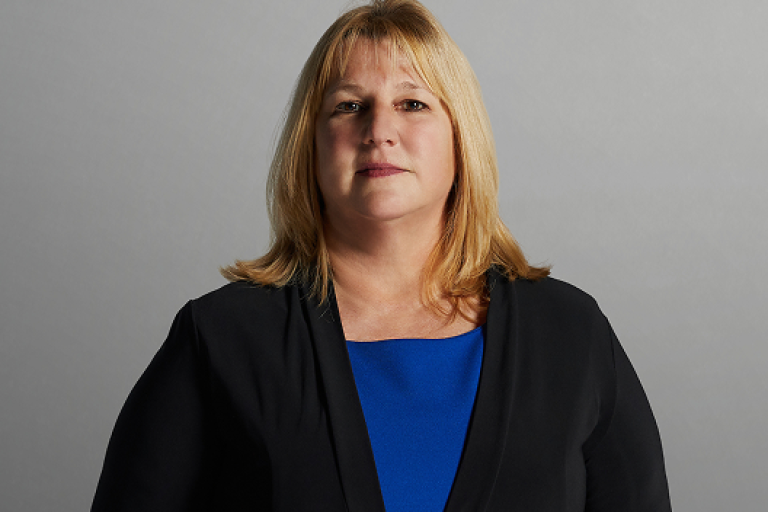
Quote from Dr. Jonathan Salik
"I tell patients, I understand why you're feeling the way you're feeling, it's because of your underlying disease process, and I want to work with you to make the diagnosis and to eventually find a treatment plan that works for you."
Get the most from your appointment
Download this guide to start a conversation with your doctor about pericarditis.
Be your own best advocate for getting the care you need. This guide includes tips to prepare for your visit, questions to ask your healthcare provider, and space to record important information such as your health history, symptoms, and triggers. Print it, fill it out, and take it with you to your visit.

Quote from Jill
"Advice I would give somebody going to see their cardiologist or primary care doctor regarding pericarditis is to write down all the symptoms you’ve had. Keep a log every single day, because you forget."

Steps to prepare for your doctor’s appointment
What do you need to discuss with your healthcare provider? This could include the symptoms of your flares, your medications, and/or how recurrent pericarditis affects your daily life.
Download and print the guide to start a conversation with your doctor provided on this website. Use it to help explain your symptoms. Have you had a flare since your last appointment? Have you experienced any new, persistent, or worsening symptoms?
Download the guide to starting a conversation with your doctor provided on this website. Review the list of symptoms listed in the guide. Think about any additional questions that you want to discuss with your healthcare provider.
Download the guide to start a conversation with your doctor provided on this website. Use it to help keep track of your healthcare provider’s answers and recommendations. Ask them if you can record the appointment using your phone so you can reference it later. You can also bring a friend or family member with you to take notes, ask questions, and help advocate for you.
Keeping an updated personal medical record can be very useful, especially if you move or change healthcare providers. Consider recording information on your flares, results of past medical tests, and any medicines you’re taking.
Be your own best advocate
Speak up
If you don’t understand a test result or something your healthcare provider says, ask them to explain it in more detail.
It’s OK to ask for specific tests or to see a specialist, such as a cardiologist, for a consultation.

Ask about a treatment plan
Managing recurrent pericarditis is an ongoing process.
Ask your doctor about treatment options and ways to manage your disease.
Quote from Carly Pearce
"It's important to share your history with your doctor because they can connect dots that maybe you don't even realize are dots."
Last updated: 04/30/25
The content on this page has been written and approved by Kiniksa Pharmaceuticals.